- Home
- Rocks
- Type fossils
- Fossil Specimens
- Minerals
- Glossary
- Stratigraphic Chart
- Michel-Levy Chart
- Classification of igneous rocks
- University of Cambridge
- Department of Earth Sciences
- ESC Library
- Moodle
- Sedgwick Museum
- DoITPoMS
- Mindat.org
- Microfossils
- Bryozoans
- Webmineral
- Tree of Life
- CrystalMaker
- Virtual Microscope
L352 - Dolomitic limestone
Specimen Age
Permian
Location
Sunderland
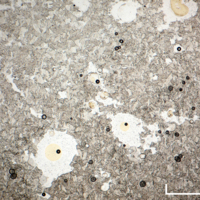
Hand Specimen
Pale buff coloured, crystalline rock.
Numerous cavities, thought to have been formed by shrinkage during alteration of primary calcite (CaCO3) to secondary dolomite (CaMg[CO3]2). There is a weak reaction to dilute acid, which suggests that there may be some calcite remaining.
Colourless crystalline material infilling holes.
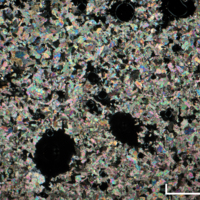
Thin-section
Almost entirely made up of very fine grains of dolomite (which tends to show more rhomb shaped crystals than calcite).
Irregular cavities into which well-developed rhomb crystals of dolomite have grown. Note that one should distinguish between the cavities in the rock (with rhombs of dolomite) and those due to the preparation of the sections.
Irregular cavities into which well-developed rhomb crystals of dolomite have grown. Note that one should distinguish between the cavities in the rock (with rhombs of dolomite) and those due to the preparation of the sections.
Rock History
It is thought that this rock was initially made-up of calcite. The alteration from calcite to dolomite, with its consequent increase in specific gravity and decrease in volume, accounts for the formation of the cavities.
Rock Name
dolmitic limestone
dolomite
magnesian limestone
dolomite
magnesian limestone